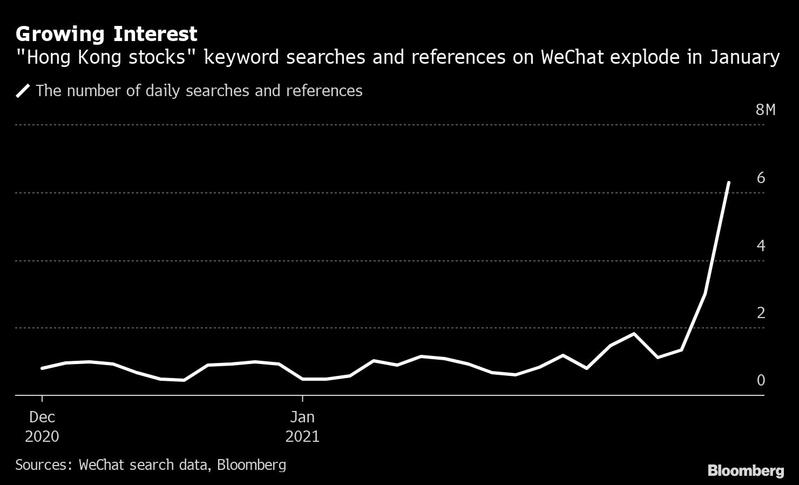
Investors on the Chinese mainland are showing unprecedented interest in Hong Kong stocks, powering the city’s fastest rally for a new year in more than three decades.
Mainland traders have bought a net US$29 billion worth of Hong Kong shares in January alone, nearing a third what they purchased in all of last year. Keyword searches and references for “Hong Kong stocks” on Tuesday reached 6.3 million on WeChat, China’s most popular instant-messaging tool, seven times the amount at the end of December, according to app data.
The benchmark Hang Seng Index has gained 9.9% this year - about three times the advance of the MSCI All-Country World Index - for its best start since 1985. The Hang Seng Index rose past 30,000 points on Thursday, the first time it breached that level since May 2019, before closing at 29,927 points
Inflows from north of the border picked up earlier this month after a US ban on some Chinese securities forced international investors to dump the likes of China Mobile Ltd. at bargain prices. Mainland buyers swooped in, broadening their targets after extreme valuations onshore encouraged a rotation into Hong Kong’s cheaper shares.
The result is a booming stock market in a city whose economy is still reeling from the effects of the pandemic and anti-government protests. The benchmark Hang Seng Index has gained 9.9 percent this year - about three times the advance of the MSCI All-Country World Index - for its best start since 1985. The Hang Seng Index rose past 30,000 points on Thursday, the first time it breached that level since May 2019, before closing at 29,927 points.
ALSO READ: Hang Seng hovers near 30,000 in best start to year since 1985
At least three brokerages said they’ve seen a surge in demand for Hong Kong stocks in recent weeks. Applications for new accounts jumped 50 percent last weekend at TF International Securities Group Ltd., according to Zhu Yunpeng, head of the firm’s securities and futures brokerage department in Shenzhen. The intense interest prompted the China Securities Journal to warn stock valuations could become disconnected from reality, leading to a correction.
Li Changmin, managing director at Snowball Wealth in Guangzhou, increased exposure of Hong Kong stocks to about 20 percent of total holdings from “very little” before last week. Li bought from Chinese brokerages that were as much as 40 percent cheaper than their mainland shares.
“Hong Kong stocks have always been cheaper, but previously you might have had to wait a long time for other buyers to follow,” Li said. “Now things are different because of the greater power of southbound flows.”
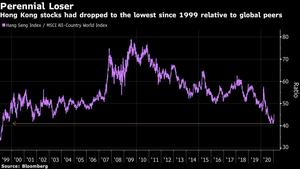
Yuan-denominated shares are on average 21 percent more expensive than their H-share equivalents, according to an index going back to 2006. The premium was at an 11-year high of almost 50 percent in October. Cheap stocks in Hong Kong last year meant southbound flows were already at a record, picking up in March as the Hang Seng Index traded below book value. But the speed and scale of purchases in January is unlike any period since the second link opened in 2016 with Shenzhen.
Traders on the mainland have limited options when it comes to asset allocation, as capital controls restrict their access to overseas securities. People on the mainland are moving more of their money into stock funds after rock-bottom interest-rates, a purge of peer-to-peer lending platforms and stagnant property prices in large cities left them with poor returns elsewhere.
But professional investors are all buying the same large caps, increasing concentration risk in the stock market and pushing valuations for the popular consumer-staples sector to the priciest since 2008. Mutual funds invested about two-thirds of their assets in only 100 stocks, according to the latest available data.
READ MORE: Mainland cash boosting HK stocks sales after record year
For some shares, southbound inflow comprises the majority of trading, accounting for 94 percent of China Mobile’s total turnover year-to-date and 74 percent for CNOOC Ltd., Morgan Stanley strategists Laura Wang, Jonathan Garner and Fran Chen wrote in a Jan 19 report. That compares to 2 percent and 3 percent in 2020, respectively, they wrote.
Along with valuations, Hong Kong’s stock market also has the strong backing of Beijing. The central government has been pushing the city as an alternative to New York as a fundraising center for mainland firms. At more than US$50 billion, the amount of capital raised in Hong Kong from initial public offerings and secondary listings last year was the most in a decade, largely from mainland companies.
Still, for some money managers, the recent run-up has a familiar feel to it. Mainland funds bought in early 2018 and in March last year, only for investors to be disappointed when Hong Kong’s stock market lagged.


