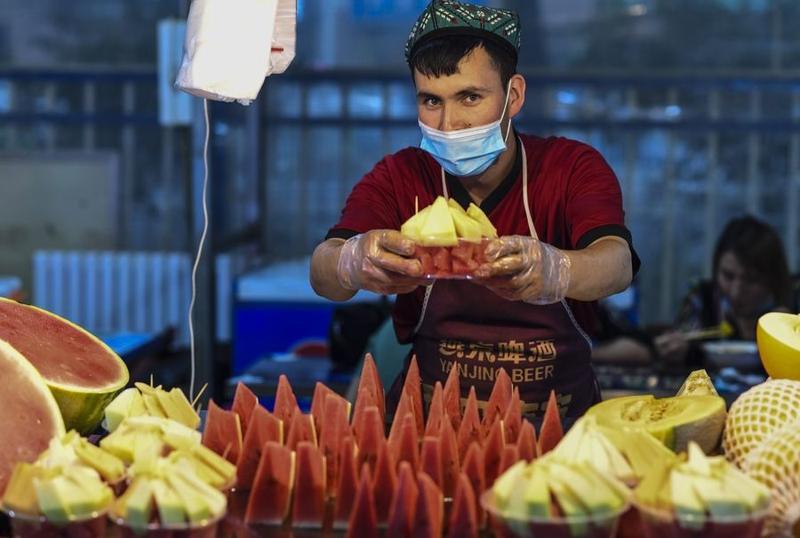
 In this May 18, 2020 photo, a vendor shows newly sliced fruits at a night fair in Hotan, Northwest China's Xinjiang Uygur autonomous region. (PHOTO / XINHUA)
In this May 18, 2020 photo, a vendor shows newly sliced fruits at a night fair in Hotan, Northwest China's Xinjiang Uygur autonomous region. (PHOTO / XINHUA)
Full of ignorance of and bias against China, some people from the US and other Western countries have recently made groundless accusations against and disseminated many fallacies about China's human rights conditions concerning Xinjiang.
Here are some of the rumors they spread, and the facts.
1. Rumor: The vocational education and training centers in Xinjiang are "concentration camps" detaining over one million Uyghurs.
Facts:
- The vocational education and training centers, established in accordance with law in Xinjiang, are no different in nature from the community corrections in the US, the Desistance and Disengagement Programme (DDP) in the UK, and the deradicalization centers in France. All of them are useful measures and positive explorations for preventive counter-terrorism and deradicalization, and are in line with the principles and spirit of the UN Global Counter-Terrorism Strategy and other counter-terrorism resolutions.
- The education and training work in Xinjiang is guided by the spirit of the rule of law as well as international principles on counter-terrorism and deradicalization. It has solid legal basis and follows well-defined legal procedures, and is done in a way that makes no linkage to any specific region, ethnic group or religion. There is no such thing as "suppression on ethnic minorities" or "persecution of Muslims".
- The claim that "nearly one million Uyghurs are detained", an outright rumor, is based on two highly dubious "studies".
ALSO READ: Bad-mouthing China a habit of the past
The first "study" was done by the US government-backed Network of Chinese Human Rights Defenders (CHRD) with interviews of only eight people. The CHRD applied the estimated ratio shown in this absurdly small sample to the whole of Xinjiang, drawing a crude conclusion that one million people were detained in the "re-education detention camps" and two million were "forced to attend day/evening re-education sessions".
The second "study" was done by a far-right fundamentalist Christian Adrian Zenz, a.k.a. Zheng Guoen. According to The Grayzone, a US-based independent news website, Zenz is a senior fellow in China studies at the far-right Victims of Communism Memorial Foundation established by the US government in 1983, and a senior member in a research group set up with the masterminding of the US intelligence community to study Xinjiang's vocational education and training centers. He believes he is "led by God" on a "mission" against China.
In September 2018, Zenz wrote an article published in the Central Asian Survey journal, concluding that "Xinjiang's total re-education internment figure may be estimated at just over one million." According to The Grayzone, Zenz based this conclusion on a single report by Istiqlal TV, a Uyghur exile media organization based in Turkey. Far from a journalistic organization, Istiqlal TV advances separatism while playing host to an assortment of extremist figures. One such character who often appears on Istiqlal TV is Abduqadir Yaqupjan, a leader of the East Turkestan Islamic Movement (ETIM). Maybe it was because the reference he cited was too absurd even to himself, that Zenz admitted that "there is no certainty" to his estimate. But Zenz "bumped up" his estimate again in November 2019, claiming China was detaining 1.8 million people.
2. Rumor: The vocational education and training centers in Xinjiang carried out "political indoctrination and intimidation" over the Uyghurs and other ethnic minorities.
Facts:
- The vocational education and training centers in Xinjiang provided courses on standard spoken and written Chinese language, legal knowledge, professional skills and deradicalization, to address the inadequate language proficiency, lack of legal literacy and job skills, as well as the varying degrees of religious extremism influence among their trainees. The purpose of the centers is to tackle terrorism and religious extremism at the root, not so-called "political indoctrination and intimidation" by any means.
- Through all-round learning, the trainees have freed themselves from the influence of terrorism and religious extremism. Their overall capacity has been improved, as evidenced by a markedly increased understanding of the law, the ability to speak and write in standard Chinese, acquisition of practical skills and the general improvement in employability. Most of them have found jobs that give them a stable income, and notably improved their families' living standards.
3. Rumor: The vocational education and training centers are poorly conditioned and lack medical facilities. The trainees are subjected to forced political indoctrination and torture, and are deprived of their rights to exercise religious customs, use local ethnic languages among others.
Facts:
- The vocational education and training centers strictly follow the basic principle of respecting and protecting human rights enshrined in China's Constitution and other laws. The trainees' basic rights and personal dignity are well protected, and insults or abuse against the trainees in any manner are prohibited. The centers fully guarantee the personal freedom of trainees. The centers are managed as boarding schools where trainees may go home on a regular basis and ask for leave to attend to personal matters, and enjoy the freedom of correspondence.
- Trainees' freedom of religious belief is fully respected and protected at the centers. Those with a religious belief can decide on their own whether to take part in legal religious activities when they are at home.
- The centers fully respect and protect the customs of all ethnic groups and provide a rich variety of nutritious halal food free of charge.
- The trainees' right to use the spoken and written languages of their own ethnicity is fully protected at the centers. All regulations, curricula and canteen menus at the centers are written in both standard Chinese and local ethnic languages.
- The centers have well-equipped facilities. Dorms are furnished with radio, television, and air conditioning or electric fans. Medical facilities are set up to provide free health counseling services and treatment for trainees. There are also venues for basketball, volleyball, table tennis and other sports, cultural venues such as reading rooms, computer rooms and cinemas, as well as venues for performances like auditoriums and open-air stages. Singing and dancing performances of different ethnic groups, sports games and other extra-curricular activities are often held to meet trainees' learning, living and entertainment needs to the greatest extent possible.
- Legal counseling rooms are set up in the centers to help address trainees' law-related difficulties and questions promptly. There are psychotherapy rooms to provide psychological counseling services and care for trainees' mental health. All trainees are covered by old-age, medical and other social insurances and free medical check-ups.
 A shop owner (left) tidies up goods in his store in Gezixiang, or "Dove Lane", in the old town of Tuancheng in Hotan, Xinjiang Uygur autonomous region, on May 27. (SADAT / XINHUA)
A shop owner (left) tidies up goods in his store in Gezixiang, or "Dove Lane", in the old town of Tuancheng in Hotan, Xinjiang Uygur autonomous region, on May 27. (SADAT / XINHUA)
4. Rumor: Detainees in the mass internment camps in Xinjiang include permanent residents of the US and Australia.
Facts:
- The vocational education and training centers in Xinjiang have never received trainees who are not Chinese nationals.
5. Rumor: Xinjiang's special operations against violent terrorist activities aim to suppress ethnic minorities under the pretext of fighting terrorism.
Facts:
- Xinjiang had suffered long and deep from terrorism and extremism. Statistics show that from 1990 to 2016, ethnic separatists, religious extremists and violent terrorists plotted and conducted several thousand violent terrorist cases and incidents, killing a large number of innocent civilians and several hundred police officers, and causing immeasurable property losses. These incidents inflicted untold sufferings on the people of various ethnic groups in Xinjiang.
- In the face of a grave and complicated counter-terrorism situation and the urgent demand from people of all ethnic groups for suppressing violence and terrorist crimes and protecting life and property safety, China's Xinjiang region has taken a series of active measures. Responding to the United Nations Global Counter-Terrorism Strategy and other counter-terrorism resolutions, Xinjiang has upheld the principle of not linking terrorism with any particular region, ethnic group or religion, and acted in accordance with the law to crack down on violence and terrorist activities that violate human rights, endanger public security, undermine ethnic unity and aim at separating the country. Since 2014, a total of 1,588 violent and terrorist groups have been taken out, 12,995 violent terrorists arrested and 2,052 explosive devices seized. Such operations have effectively curbed the rising trend of frequent terrorist activities and protected people's right to life, right to health, right to development and other basic rights to the maximum extent. These measures have received full support from people of all ethnic groups in Xinjiang.
- Through law-based counter-terrorism, deradicalization and vocational education and training, Xinjiang has not seen a single violent terrorist case in the past three-odd years. Extremist infiltration has been effectively curbed, public security significantly improved and people's sense of fulfillment, happiness and security markedly enhanced.
- In October 2019, more than 60 countries spoke in support of China's Xinjiang policy at the United Nations General Assembly. Among them, over 30 are Islamic countries. In contrast, none of the few countries criticizing China's Xinjiang policy are Islamic countries.
- Since late December 2018, more than 1,000 people from over 90 countries visited Xinjiang in 70-plus groups. They include UN officials, foreign envoys to China, representatives of relevant countries to Geneva, journalists and members of religious groups. After their visits, they expressed the view that Xinjiang's counter-terrorism and deradicalization efforts are in line with the purposes and principles of the UN in fighting terrorism and upholding basic human rights and that these efforts deserve to be fully recognized and emulated by others.
6. Rumor: China restricts the freedom of communication and movement of Uyghurs in Xinjiang in the name of counter-terrorism and deradicalization.
Facts:
- Xinjiang has never restricted the freedom of movement of Uyghurs or people of any other ethnic group. In Xinjiang, anyone from any ethnic group, except those prohibited from leaving the country for suspected crimes, can exit and enter China freely. Several hundred thousand people from Xinjiang are now overseas.
- Xinjiang has never restricted Uyghurs or people of other ethnic groups from contacting their overseas relatives. They can do so not only through international phone calls, but also through voice and video chats on instant messaging apps such as WeChat and QQ. They can also do business and trade with people in other countries through various communication means.
7. Rumor: Xinjiang conducts large-scale surveillance on local ethnic minorities.
Facts:
- It is an international common practice to harness modern technology and big data in improving social governance. For example, there were 4.2 million surveillance cameras installed in the UK as early as 2010, the highest number in the world then. Today the country has about six million cameras, one for every ten people. In the United States, facial recognition is conducted in the top 20 airports against passengers. The city surveillance system built by New York police has devices covering every neighborhood of the city watching people and vehicles on the street and tracking and screening information on people's mobile phones. What Xinjiang has done in this respect pales significantly in comparison with these two countries.
- The cameras in urban and rural public places, main roads and transport hubs in Xinjiang are installed in accordance with the law for the purpose of improving social governance and forestalling and combating crimes. These measures make people feel safer and are widely supported by people of all ethnic groups. The measure does not target any specific ethnicity, not to mention that cameras by themselves identify or target no specific ethnicity. They are there to deter bad guys and protect good people.
 In this Aug 18, 2019 photo, locals chat with each other in a renovated house in Kashgar, Xinjiang Uygur autonomous region. (PHOTO / XINHUA)
In this Aug 18, 2019 photo, locals chat with each other in a renovated house in Kashgar, Xinjiang Uygur autonomous region. (PHOTO / XINHUA)
8. Rumor: Mass forced labor against ethnic minorities is taking place in Xinjiang.
Facts:
- According to a US news website the Greyzone, the forced labor stories were in fact a PR blitz orchestrated by anti-China forces from the US and Australia.
- The stories were cooked up by the Australian Strategic Policy Institute (ASPI) which has long been funded by the US government and American arms dealers. To serve the interests of its sponsors, the institute blatantly spread disinformation to vilify and demonize China, particularly on Xinjiang-related issues. Together with anti-China forces in the US, the ASPI made up baseless and biased stories to smear and attack Xinjiang's counter-terrorism and deradicalization efforts. The institute has no credibility whatsoever. Former Australian Ambassador to China Geoff Raby sees the ASPI as "the architect of the China threat theory in Australia". Former Qantas Airways CEO John Menadue said the institute "lacks integrity and brings shame to Australia".
- Ethnic minority workers from Xinjiang are part and parcel of the country's labor force. They have the rights to be employed, sign labor contracts, obtain labor remunerations, take rest and vacations, acquire labor safety and health protection, and enjoy social insurance and welfare as prescribed by law. They have the freedom to choose their occupation. Their personal freedom has never been restricted.
- There are only limited job opportunities in the four southern Xinjiang prefectures (Hotan, Aksu and Kashi prefectures, and Kizilsu Kirgiz autonomous prefecture) as industrialization and urbanization there are underdeveloped. The government of the Xinjiang Autonomous Region has taken measures based on the wishes of local people to help them find jobs in their hometowns, nearby cities or other areas of Xinjiang, or in the provinces and cities that have pair-up assistance programs with Xinjiang, thus ensuring peoples' right to work to the maximum extent. Since 2018, Xinjiang has helped 151,000 surplus rural workers from poor families in the southern prefectures to find employment elsewhere. With an average annual income of over 45,000 yuan, these workers have all been lifted out of poverty.
- China has been improving its legal system and its State Council has established an inter-agency mechanism to crack down on crimes such as human trafficking and forced labor. Such efforts have proven effective. China earnestly fulfills its international obligations and has ratified 26 international conventions on human rights. China will continue to strengthen exchanges with all parties and fight forced labor and other crimes together.
9. Rumor: Xinjiang has demolished a large number of mosques.
Facts:
- Xinjiang has seen sound development of the religion of Islam. The number of mosques in Xinjiang has grown from some 2,000 at the beginning of reform and opening-up in the late 1970s to 24,400 today, more than 10 times that in the United States. In Xinjiang, there is a mosque for every 530 Muslims on average.
- Xinjiang takes the preservation and maintenance of mosques very seriously. Some cramped and dilapidated mosques, those with poor layout designs and those inconvenient for religious activities have been rebuilt, relocated or expanded in light of the needs and wishes of local Muslim communities. Such adjustments have been welcomed by religious leaders and believers.
10. Rumor: Graveyards of ethnic minorities are demolished in parts of Xinjiang.
Facts:
- Under the regulations of the local authorities, the government does not promote cremation for ethnic minorities observing traditional ways of interment. On the contrary, it takes concrete measures to help preserve the tradition, by designating burial ground and building dedicated cemeteries. Besides, there is no restriction on other ethnic customs followed in weddings, funerals, and name-giving ceremonies.
11. Rumor: The "Pair Up and Become Family" program is designed to monitor ethnic minorities in Xinjiang.
Facts:
- Since 2016, an extensive ethnic unity campaign has been conducted among government officials and people of different ethnicities in Xinjiang. Some 1.1 million officials have paired up and made friends with 1.6 million local people, treating each other like family members. They have respected and helped each other, and forged deep bonds through close interactions. The officials leveraged their expertise to help local people explore ways to shake off poverty and address difficulties in their lives, such as access to medical services, job opportunities and education. The campaign, with its real, substantial benefits to the public, has been well received by the people of all ethnic groups.
12 Rumor: The local government sends Uyghur children to boarding schools and separates them from their parents.
Facts:
- The boarding school system is an effective means to improve education in China's remote areas and ease the burden on students and their families. In Xinjiang, students of all ethnicities attend schools closest to their homes. Those living near the campus can be commuter students. For those living further away, schools provide them with free accommodation, plus free meals for those from rural families. It is up to the students and their parents to decide whether to live on or off campus.
 13. Rumor: The Chinese government forces sterilization, abortion and birth control on Uyghurs and other ethnic minorities in Xinjiang.
13. Rumor: The Chinese government forces sterilization, abortion and birth control on Uyghurs and other ethnic minorities in Xinjiang.
Facts:
- The Chinese government protects the lawful rights and interests of all Chinese without distinction of ethnicity. Over the years, the Uyghur people and other ethnic minorities have enjoyed a preferential population policy. In the four decades between 1978 and 2018, the Uyghur population in Xinjiang increased from 5.55 million to 11.68 million, accounting for 46.8% of the total population of the autonomous region.
- To put things into perspective, let's look at the situation in the United States. Racial and ethnic minorities in the US have long been the targets of bullying, exclusion, and widespread and systemic discrimination in the political, economic, cultural and social aspects of their lives. Take Native Americans as an example. For quite a long period of time, the US government had been enforcing a policy of genocide, segregation and assimilation against Native Americans. For nearly a century after its founding, the US was uprooting and killing American Indians in its Westward Movement. The Native American population plunged from 5 million in 1492 to 0.25 million in the early 20th century. It now accounts for a mere 2 percent of the US population. Another example, African Americans. African Americans have a COVID-19 infection rate five times that of white Americans, and a much higher mortality rate as well. This highlights the racial inequality in the US. The recent death of an African American George Floyd and the massive protests that followed once again shows that the systemic racial discrimination in the US has reached a point where racial and ethnic minorities "can't breathe". It calls for an urgent solution.
14. Rumor: The Chinese government's brutal crackdown on Muslims is a human rights violation not seen since World War II.
Facts:
- One of China's five ethnic minority autonomous regions, the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region is home to 25 million people of different ethnic groups who live and work in harmony. Among them, ten ethnic groups, including Uyghur and Hui, consist mainly of Muslims. The Muslim population has been growing steadily, accounting for nearly 60% of the total local population.
- Under a system of ethnic regional autonomy, China treats all ethnic groups equally and pursues prosperity and development for people of all ethnicities. It ensures that ethnic autonomous areas exercise the power to self-govern in accordance with law, and protects the legitimate rights and interests of ethnic minorities. In Xinjiang, every chairperson of the People's Congress, the autonomous regional government, and the CPPCC regional committee is from ethnic minority groups. Ethnic minorities take 64.2 percent of the seats in the 13th Xinjiang People's Congress, and 46.7 percent of the seats in the 13th CPPCC Regional Committee of Xinjiang.
- Xinjiang fully implements the policy of freedom of religious belief. The freedom of religious belief of all people, regardless of their ethnicity, is fully protected in accordance with law. Believers and non-believers enjoy the same political rights and economic, social and cultural rights.
- On 25 May, George Floyd, an African-American, was killed in Minneapolis in a brutal assault by a white police officer. His death triggered massive demonstrations and protests across the country, throwing into sharp relief the public outcry and anger over the systemic racism long in existence in the country. The UN Human Rights Council held an urgent debate and adopted a resolution voicing strong condemnation and urging concrete measures from the US to protect human rights and fundamental freedoms of Africans and of people of African descent.
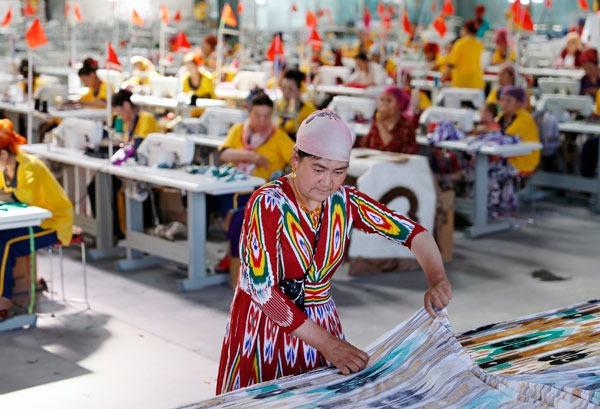 In this undated photo, seamstresses at work at a sewing factory in Xinjiang Uygur autonomous region. (PHOTO / XINHUA)
In this undated photo, seamstresses at work at a sewing factory in Xinjiang Uygur autonomous region. (PHOTO / XINHUA)
15. Rumor: The Chinese government uses COVID-19 to "wipe out" Muslims.
Facts:
- Thanks to the joint efforts of the people of all ethnic groups in Xinjiang, COVID-19 has been effectively contained in the region. As of 29 June, a total of 76 confirmed cases had been reported in Xinjiang, including 73 cured cases and three deaths. With no new confirmed cases for over 130 days, Xinjiang has resumed full normalcy in economic and social activity early on and is back on track for economic and social development.
- On 9 December 2019, Shohrat Zakir, Chairman of the Government of Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, announced that all the trainees at the vocational education and training centers had completed their studies. There is no risk of cluster infections at these centers.
16. Rumor: In media reports or social media posts about "missing persons", overseas Uyghurs tell stories about their "families" and "friends" in Xinjiang who have "lost contact" or "gone missing".
Facts:
- Xinjiang has never curtailed the freedom of travel of Uyghur people or people of any other ethnic groups. Nor is there any restriction on communication with relatives abroad.
- It has been verified by the relevant authorities that the so-called "missing persons" mentioned by overseas East Turkistan elements are either living a normal life or simply non-existent.
In an ABC News (Australia) report, Azmat Omar, a Chinese citizen living in Australia, claimed that he had lost contact with his family members in Xinjiang, including his father, stepmother, three brothers, two sisters and over 20 nephews. It later became clear that all his family members in China are living normal lives and enjoy full personal freedoms.
During a UN Human Rights Council session in February 2020, the World Uyghur Congress put up photos of the so-called "Uyghurs persecuted by the Chinese government" in the square with the Broken Chair in front of the Palace of Nations in Geneva. The photos have proved to be fake. Separatist groups got hold of the pictures and personal information of Uyghur officials and residents living normal lives in Xinjiang and misrepresented them to spread rumors.
17. Rumor: China uses denial of passport renewal as a weapon to force overseas Uyghurs to return to China, where they face extrajudicial detention.
Facts:
- In China, a country governed by the rule of law, the citizens' personal freedom and right to leave and enter the country are protected by law. Chinese diplomatic missions abroad protect the lawful rights and interests of overseas Chinese, including ethnic minorities from Xinjiang, in accordance with laws and regulations including the Exit and Entry Administration Law of the People's Republic of China and the Passport Law of the People's Republic of China. Anyone who holds the Chinese nationality, recognizes oneself as a Chinese national, and has not violated Chinese laws and regulations can apply to the Chinese embassy or consulate in the place of residence for passport renewal or re-issuance.
- Xinjiang follows a fact- and law-based approach in managing exit and entry affairs and cracking down on crimes of violence and terrorism and activities of religious extremism. Most applications for passport renewal or re-issuance from Xinjiang natives have been received and approved by Chinese embassies or consulates. The very few who have their applications rejected are suspected of involvement in terrorist activities in violation of Chinese laws and regulations.
18. Rumor: The research paper titled The Karakax List:
Dissecting the Anatomy of Beijing's Internment Drive in Xinjiang
Facts:
- The so-called research paper was produced by Adrian Zenz, a key figure in the so-called Xinjiang's Internment Camps Research Group set up and controlled by US intelligence agencies. The paper is based on a name list of "students sent to re-education who are family members of those who went abroad and have not returned." The list itself was cooked up by ETIM members from inside and outside China.
- The majority of the 311 people on the list live in Bostan Street in Moyu (Karakax) County. They live and work just like most other people do, and have never received vocational education and training. Only a very small number of those on the list have been sent to vocational education and training in accordance with the law for being influenced by religious extremism and committing minor crimes. Only 19 out of the 311 people have relatives abroad, but none of them have received the vocational education and training.
19. Rumor: 30 relatives of Rebiya Kadeer have been detained without trial.
Facts:
- No one from Rebiya Kadeer's family has been implicated. All her relatives live and enjoy freedom in Xinjiang. They want her to stop spreading lies and disturbing their peace.
20. Rumor: Family members of Furqat Jawdat, Arapat Arkin, Zumrat Dawut and other so-called "activists" have been "harassed, imprisoned or arbitrarily detained."
Facts:
- Both Furqat Jawdat and Arapat Arkin are members of the World Uyghur Congress, an organization notorious for its violent, terrorist and separatist agenda. They make a living by fabricating stories and splitting their motherland. Their relatives, who are leading a normal life in Xinjiang, feel ashamed of having people like them in the family.
- Furqat Jawdat's mother is living a normal life in Xinjiang and has regular contact with him.
- Arapat Arkin's father was sentenced for taking part in violent and terrorist activities, but his mother and younger brother and sister are all living a normal life. None of them have been taken into custody. His mother has repeatedly urged him not to follow his father's path, "Your father did harm to our society. He is being punished for his wrongdoing. He is very sorry for what he has done. So please stop telling lies and leave the World Uyghur Congress before it's too late."
- Regarding the claim that "Dawut's elderly father, who had been detained and interrogated multiple times by the local authorities in Xinjiang, recently passed away under unknown circumstances", here is what really happened: Dawut's father had been living with his children all these years, without ever being "interrogated" or "detained". Suffering from a serious heart condition for many years, the octogenarian passed away in hospital in October 2019 after all medical treatment had failed. During his last days in hospital, the old man was attended by Dawut's older brothers and other relatives who stayed by his bedside.
21. Rumor: Mutallip Nurmamat died nine days after his release from an internment camp. Prominent Uyghur writer Nurmamat Tohti died in an internment camp. Sayragul Sawutbay saw people tortured in a detention camp before fleeing China. Uyghur musician and poet Abdurehim Heyit was sentenced to eight years in prison and died in the second year of imprisonment.
Facts:
- Mutallip Nurmamat never studied in a vocational education and training center. In December 2018, he died from acute alcohol poisoning, alcoholic encephalopathy, respiratory failure and acute upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage triggered by alcohol abuse.
- Nurmamat Tohti never studied in a vocational education and training center. He had had coronary artery disease for over 20 years and spent most of his time receiving treatment in hospital or recuperating at home. On 31 May 2019, after suffering an acute myocardial infarction at home, he was taken to hospital but passed away despite emergency rescue efforts.
- Sayragul Sawutbay is suspected of fraud. To flee justice, she crossed the border illegally into Kazakhstan. She never stayed in any vocational education and training center in China, and was never detained before her illegal escape. Her words about seeing people tortured cannot be true.
READ MORE: Double standard of West on HK and Xinjiang has been exposed
- Abdurehim Heyit, arrested on suspicion of endangering national security, is in good health. On 10 February 2019, Heyit said in a published video, "I am under investigation for suspected violations of law. I am in very good health, and I have never been abused."
22. Rumor: A comic book titled What has happened to me: A testimony of a Uyghur woman recounts the experiences of Mihrigul Tursun, a Uyghur woman who allegedly escaped a vocational education and training center. She claimed to have seen the death of nine women while in custody, and that her younger brother was abused to death in a vocational education and training center.
Facts:
- Mihrigul Tursun, an ethnic Uyghur, used to live in Qiemo County of Bayingol Mongolian Autonomous Prefecture in Xinjiang. She was detained for 20 days in April 2017 by the Public Security Bureau of Qiemo County over suspicion of inciting national enmity and discrimination. In 2018, she voluntarily relinquished her Chinese citizenship and left China with an Egyptian passport. She had never been imprisoned in China, nor had she studied in any vocational education and training center.
- Akbar Tursun, her younger brother, said publicly, "My sister Mihrigul is full of lies. She not only said I am dead, but also lied about seeing others die."


